Mathematics
THIS PAGE IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION- WE HAVE INTRODUCED A NEW SCHEME THIS TERM- ‘CAN DO’ MATHS- MORE INFORMATION TO FOLLOW…

Talk (Oracy)
- Mathematical talk and the use of specific vocabulary is planned for at every stage of learning.
- Children use partner work to discuss ideas and use given vocabulary, ready to share with the class.
- Stem sentences are used for the children to build model answers upon and to support their mathematical understanding.
“There are ___ equal groups of ___.”
“The whole is ____. It has been divided into ___ equal parts .”
Mastering Number Reception, Y1 and Y2.
Mastering Number is a programme offered by the National Centre for Excellence in the Teaching of Mathematics (NCETM) and the Maths Hubs Network. It aims to develop solid number sense, including fluency and flexibility with number facts, which will have a lasting impact on future learning for all children.

Ways to help at home
1 minute maths app- https://whiterosemaths.com/resources/1-minute-maths This FREE app does not require a log in and has different levels of games which last for 1 minute, focussing on fluency and automatic recall. Your teacher will direct you to which games to play.
White Rose Maths Home Learning Lessons: https://whiterosemaths.com/homelearning?year=year-1
You can select your year group to watch FREE teacher led videos of maths concepts. The teaching in these videos is very closely matched to how we teach in school.
Times Tables Rockstars: https://ttrockstars.com/
How quickly can you answer the tables set?
Maths Bot: Online versions of our practical maths equipment
https://mathsbot.com/manipulatives/blocks (Base 10)
https://mathsbot.com/manipulatives/fractionWall (Fraction Wall)
https://mathsbot.com/manipulatives/rekenrek (Rekenrek KS1)
There are lots of examples on Maths Bot you could use at home. Just click the home icon to find more.
What is teaching for mastery?
- Mastering maths means pupils of all ages acquiring a deep, long-term, secure and adaptable understanding of the subject.
- The phrase ‘teaching for mastery’ describes the elements of classroom practice and school organisation that combine to give pupils the best chances of mastering maths.
- Achieving mastery means acquiring a solid enough understanding of the maths that’s been taught to enable pupils to move on to more advanced material .
(National Centre for Excellence in the Teaching of Mathematics).
Elements of Mastery classroom practise and school organisation are based on The 5 Big Ideas. These are built into the Power Maths programme.
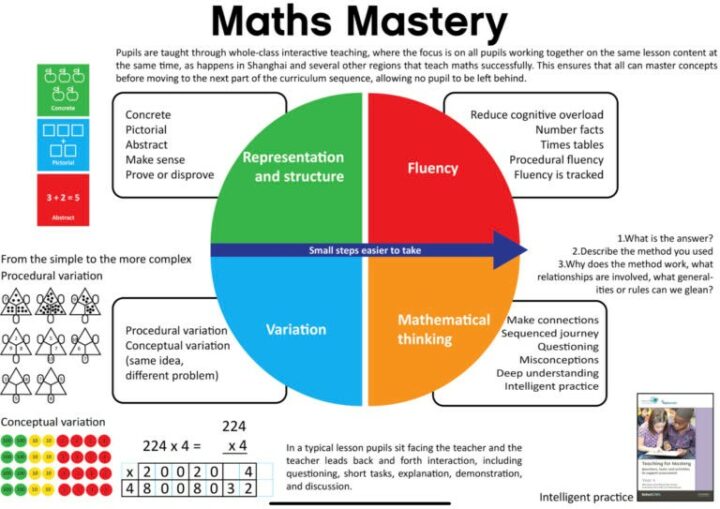
A great deal of research over many years has provided us with the knowledge of how best to teach maths. We are following research from the top performing countries across the world such as China and Singapore.
Teaching Maths for Mastery: Introduction from NCETM on Vimeo.
What is Teaching for Mastery by Debbie Morgan, Director of Primary Mathematics NCETM
Maths Anxiety
- Research says that maths anxiety compromises the functioning of working memory (Ashcroft and Krause 2007).
- It has been proven that maths anxiety directly links to poor performance in the subject.
- It is different to test anxiety and general anxiety. Math anxiety is not hereditary; no one is born as a bad mathematician.
- Adults own perception and experiences of maths can influence children.
- Children pick up on how you talk about it, for example, responses towards homework ‘Oh Mummy is rubbish at maths’ or Maths just isn’t me’.
- Here are some ways you can change mindsets and support children:

At Two Gates, we support reducing maths anxiety by removing time pressures on learning where possible. Time is important, and quick recall is necessary. However, pace of learning and varying practise tasks are carefully designed to support children not to feel overwhelmed when on their learning journey.
In addition, we use tools such as manipulatives to reduce the demand on the working memory. At home, you can use items such as pasta, toy cars and Lego to support learning. Children can also use pictures and pictorial representations to unpick and understand the maths.
Other ways to reduce children’s anxiety include using breathing techniques and helping children express how they are feeling and learn to self-regulate their emotions:

